Start by calling us so we can discuss your needs and offer professional feedback about the Crypto concept.
Crypto Developments
Web crypto development company, Best crypto development agency
Our Company has the resources and can help with Cryptocurrency based developments.
Our techs have helped develop some of the most renowned crypto coins in the world and we can help you to resolve your Cryptocurrency development end goal.
We have resolved proof of concepts that have revolutionised sectors in the crypto space.
In an ever improving arena, we look forward to our next Crypto challenge and devising the ultimate solution for your Crypto Company’s extravagant claim of dominance!

What is the process for Crypto developments?
Once we have agreed on the Crypto concept and have the details firm, we will quote to you holistically to include the detail, a mock design if practical and required, the timeline, the terms and the price. At this point we have the freedom to discuss the Crypto development proposal and make changes so that both parties are clear and happy with the proposal.
Once we have the agreement in place, the initial cleared payment will authorise the prompt commencement. Your project manager will report to you in an agreed format, or as required if we should seek feedback or approvals to continue. Once the project is complete and approved and paid we will handover the files for your keeping whereby we recommend backing up those files, or we can assist with hosting the project for you, as per the terms of the arrangement.

How much does crypto development cost?
As a ballpark: To develop a token can be relatively cheap from $3k where as the development of a blockchain could take a team of technicians many months and range from $80k to much higher. Add peripheral costs such as website, branding, hosting, insurance, legals, and subscription fees.
Understanding Crypto Development
The crypto space is growing so quickly it can be hard to keep up just on a trading level, let alone to start to ponder how to develop your own Crypto project. We hope that the below information will help to declutter some of the mystery and draw focus to the elements at play to hone in on a strategy for your desires. Bear in mind there are many scenarios and this outline is not exhaustive but it's a good start.
NETWORKS
Networks/blockchains - They distribute a ledger among many and use the network to prove that exchanges occured.. public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains and hybrid blockchains.
Nodes - All nodes on a blockchain are connected to each other and they constantly exchange the latest blockchain data with each other so all nodes are able to update. They spread, store and preserve the blockchain data, a blockchain exists on nodes. Nodes are often mentioned in regard to 'peer nodes' whereby the node is the individual computer in the chain of computation. You can think of the node as the server that holds the block computation.
EVM Ethereum Virtual Machine - it executes code; the runtime environment for every smart contract, an instance/existance created by many machines. EVM is the thing that manages the computations for every block state in the Ethereum protocol. Each block in the Ethereum chain has only one canonical state. The purpose of the Ethereum block chain is to run this machine in a continous state and record there all its accounts and smart contracts.
Protocol - Is the set of rules that a blockchain subscribes to.
PUBLIC network/blockchain - Anyone can be involved and mine, validate, bug find and change its (usually open-source) code but no validated data/exchange can be changed. For electronic notarization of affidavits and public records of property ownership. Ideal for organizations that are built on transparency and trust, such as social support groups or non-governmental organizations. Because of the public nature of the network, private businesses will likely want to steer clear. Transparent, slow, secure for all users. Hyperledger for example is a popular global enterprise blockchain project that offers users the necessary framework, standards, guidelines, tools and so forth to build open-source blockchains and related applications for use across various industries.
PRIVATE network/blockchain - Operates like a public blockchain network in the sense that it uses peer-to-peer connections and decentralization, this type of blockchain is on a much smaller scale though naturally. Instead of just anyone being able to join and provide computing power, private blockchains typically operate on a small network inside an organization. Known as permissioned blockchains or enterprise blockchains. Think of it as the intranet, as opposed to the public blockchains are more like the internet. Because they're limited in size, private blockchains can be fast and can process transactions faster than public blockchains. Less nodes than public block chain so therefore less copmpounding of security. There is no anonymity on private block chain and lacks transparency. Use-cases: trade secret management, auditing, supply chain management, asset ownership and internal voting. Fast scalable secure for founder and controled.
HYBRID network/blockchain - Typically, transactions and records in a hybrid blockchain are not made public but can be verified as needed, such as by allowing access through a smart contract for example. Confidential information is kept inside the network but is still verifiable. Even though a private entity may own the hybrid blockchain, it cannot alter transactions. Some elements could be public and some private. When a user joins a hybrid blockchain, they have full access to the network. The user's identity is protected from other users, unless they engage in a transaction. Then, their identity is revealed to the other party. One of the big advantages of hybrid blockchain is that, because it works within a closed ecosystem, outside hackers can't mount a 51% attack on the network. It also protects privacy but allows for communication with third parties. Transactions are cheap and fast, and it offers better scalability than a public blockchain network. This type of blockchain isn't completely transparent because information can be shielded. Upgrading can also be a challenge, and there is no incentive for users to participate or contribute to the network. Real estate companies for example can use a hybrid blockchain to run systems privately but show certain information, such as listings, to the public. Retail can also streamline its processes with hybrid blockchain, and highly regulated markets like financial services can also see benefits from using it. Medical records can be stored in a hybrid blockchain whereby the record can't be viewed by random third parties, but users can access their information through a smart contract. Governments can also use it to store citizen data privately but share the information securely between institutions. Fast scalable, some private some public, difficult to upgrade.
CONSORTIUM network/blockchain - Like hybrid but multiple organizational members collaborate on a decentralized network. It's a private blockchain with limited access to a particular group, eliminating the risks that come with just one entity controlling the network on a private blockchain. the consensus procedures are controlled by preset nodes. It has a validator node that initiates, receives and validates transactions. Member nodes can receive or initiate transactions. Fast scalable secure with flexible control. It can still be compromised if a member node is breached. Use cases. Banking and payments are two uses for this type of blockchain. Different banks can band together and form a consortium, deciding which nodes will validate the transactions. Research organizations can create a similar model, as can organizations that want to track food. It's ideal for supply chains, particularly food and medicine applications. Hybrid for the purposes of group corporate integrations.
CONSENSUS ALGORITHMS
POW - Proof of work is a form of cryptographic proof (a 'hash' or long string of characters that matches a target hash for the current block) in which one party (the prover) proves to others (the verifiers) that a certain amount of a specific computational effort has been expended. Verifiers can subsequently confirm this expenditure with minimal effort on their part. Proof of work is fundamental to Ethereum and Bitcoin's basic use case of being a store of value that can be securely and trustlessly transferred without censor. (PoW) describes a system that requires a not-insignificant but feasible amount of effort in order to deter frivolous or malicious uses of computing power, such as sending spam emails or launching denial of service attacks.
PoUW - Proof of Useful Work is a novel blockchain consensus protocol used to improve efficiency and security of blockchain. Classical Bitcoin mining is a wasteful and resource- intensive process as its Proof of Work (PoW) protocol resembles a lottery and the underlying computational work is not useful otherwise.
POS - The Proof of Stake concept states that a person can mine or validate block transactions according to how many coins they hold. This means that the more coins owned by a miner, the more mining power they have. The whole process uses marginally more energy than a computer would if it was just on which could be referred to as a 'ubuiquitous' process. Some believe that the result is that energy consumption and computational cost for proof of stake is 99.99 percent lower than proof of work. It can be seen as unfair though because it concentrates on power among a small group of people. It is more centralized since on Ethereum only a minimum of 128 validators participate in mining new blocks; this could allow for manipulation and collaboration on the network, making it unreliable. However as a reference, Ethereum has surpassed 200k validators and Avalanche, as another example has surpassed 4k. Cardano and Avalanche, among others are popular POS blockchains and Ethereum 2 is heading towards it.
sPoS - Secure Proof of Stake, Elrond has proposed a novel approach to consensus called “Secure Proof of Stake” which eliminates PoW computational waste, and combines eligibility through stake and rating with random validator selection, and an optimal dimension for the consensus group.
PoI - Proof of Importance is a cryptocurrency term defined as a blockchain consensus technique – essentially, proof of importance works to prove the utility of nodes in a cryptocurrency system, so that they can create blocks.
GENERAL CRYPTO DEVELOPER JARGON
Exchange Developments A crypto exchange is a platform on which you can buy and sell cryptocurrency. You can use exchanges to trade one crypto for another — converting Bitcoin to Litecoin, for example — or to buy crypto using regular currency, like the U.S. Dollar. Exchanges reflect current market prices of the cryptocurrencies they offer. If you develop an exchange you will likely need to develop a wallet app for that exchange also.
Crypto Assets (all electronic money). Digital currencies are intangible e-money, sometimes regulated, sometimes unregulated. ... Some characteristics make a currency more cryptographic vs a virtual one: encryption/cryptography allowing privacy, pseudonymity or anonymity.
Regulation The sale of cryptocurrency is generally only regulated if the sale (i) constitutes the sale of a security under state or Federal law, or (ii) is considered money transmission under state law or conduct otherwise making the person a money services business (“MSB”) under Federal law.
Coin Developments A native cryptocurrency or digital currency that operates within a specific financial system on a unique blockchain.
Token Developments Can be cheaper, faster, and easier to develop than coins. They require no maintenance but come with dependence on the main network, which gives little to no flexibility. Tokens may work as side projects that bring funds to the main business, or in any way that they represent real assets that can be moved around without physically touching them.
Coins/Tokens Coins are just method of payment while tokens may present a company's share, give access to product or service and perform many other functions. Coins are currencies that can be used for buying and selling things. You can buy a token with a coin, but not vice versa. As for investors, you first need to know that both tokens and coins can be traded on exchanges as long as they are listed. The difference comes in usage cases. A coin usually has money utility. And if you want to invest in one, not for the sake of exchanging it later but to use it, then make sure there are vendors who actually accept that cryptocurrency. On the other hand, tokens can still be used inside the DApps they are meant for even when they have no other utility.
51% Attack A 51% attack (AKA Majority Attack) is an attack on the blockchain by one or more miners who own more than 50% of the network’s mining hashrate or computational power. A coin may be susceptible to a 51% attack, especially in the early stages of formation; if it’s built on a pre-existing network though, it isn't likely.
Wallet Developments A cryptocurrency wallet is an 'app' that allows cryptocurrency users to store and retrieve their digital assets. When a user acquires cryptocurrency, such as bitcoins, they can store it in a cryptocurrency wallet and from there use it to make transactions. The different types of wallet 'app' that can be developed are much the same as any other standard development such as Browser, desktop software, mobile app, external hardware and, paper with QR code.
Gas Fees Are the charges applied to token trades for the cost of processing the associated smart contracts.
Staking/Rewards Staking is a way to put your crypto to work and earn rewards on it. ... Staking cryptocurrencies is a process that involves committing your crypto assets to support a blockchain network and confirm transactions. It's available with cryptocurrencies that use the proof-of-stake model to process payments.
Wrapping When you wrap a staked coin it prevents the reward from visibly dropping as frequently as the reward normally drops. Droping the reward becomes a manual process. By wrapping the coin as such your tax laws may or may not see that as taxable only when it manually drops, rather than when it ought to have dropped.
dApps digital applications that run on a blockchain network of computers instead of relying on a single computer. ... Benefits of dApps include the safeguarding of user privacy, the lack of censorship, and the flexibility of development.
DOA / DAC A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), sometimes called a decentralized autonomous corporation (DAC), is an organization represented by rules encoded as a computer program that is transparent, controlled by the organization members and not influenced by a central government.
ICO An initial coin offering (ICO) is the cryptocurrency industry's equivalent to an initial public offering in the stock market (IPO). A company looking to raise money to create a new coin, app, or service launches an ICO as a way to raise funds. Through ICO trading platforms, investors receive unique cryptocurrency "coins" (currency) or “tokens” (agreements) in exchange for their monetary investment in the business.
IEO In IEO companies directly sell their tokens in the exchange to individual participants without offering them in an ICO.
IDO IDO is a special case of IEO. The main difference between IEO and IDO is that IDO is definitively executed on a decentralized exchange.
AI can work in tandem with blockchain to solve many of the problems. More accurate predictions, sentiment research on the crypto markets, automated trading, and superior investment insights.
Accepting BTC as payment This is something we get asked about a lot and there are a number of third-party providers with the option to enable payment through digital currencies from within your existing applications. The three that we are engaging most frequently lately are – Blockonomics, BitPay & Coinbase. They have slight differences. If you wish to get the payment converted into fiat and sent to your bank account, go for BitPay or Coinbase, and if you wish to send funds to the exchange market or bitcoin wallet, opt for Blockonomics.
Crypto Website vs Standard Website a Crypto website is estimated to potentially take more than 5 weeks, we have to use React.js to implement all the required points. We need to connect the website backend to the crypto blockchain network. There are many technical barriers. The website has many functions that general dapp sites don't have. We need to combine normal payment methods with crypto logic. The website can in fact be the most labour-intensive/technical part of all the development peices of your standard over-arching crypto development. how mHere's a detailed breakdown of the website development. 1. Writing ERC20 Token Smart Contract - Total Supply - Number of tokens to be issued, Token Name, Symbol, Cryptocurrency Name and Symbol, Other Token Strategy, Other Functions *1 Day* | 2. Webpage UI Design - A document that specifically describes the pages to be present or an Overview document is required prior to commencement. Either by you or by us so easier/better if it's by you. *7 Days* | 3. Combine Cryptocurrency And Webpage - We combine a web page with a platform for issuing, presale & ICO of newly created tokens (your tokens). *3 Days* | 4. Tokenomics - Implement the logic for Tokenomics. *5 Days* | 5. Other Token explorer - This shows the price and comparison tables of different tokens. Here, it shows the price ratio between Tokens (ether, bsc, dogedash, ...) of various networks (Ethreum, Binanse, ..) and your token. *4 Days* | 6. Testing *7 days* | TOTAL 27 days (That's not just 1 individual involved.)
Blockchain Forking There are many reasons for forking a blockchain. It is essentially a re-routing of the procedural chain of events which could be used for protocol changes, security, reverting periods or re-designing the blockchain for an alternate purpose. The below image is a developers guide to the development of an Olympus DAO fork segment in a project.
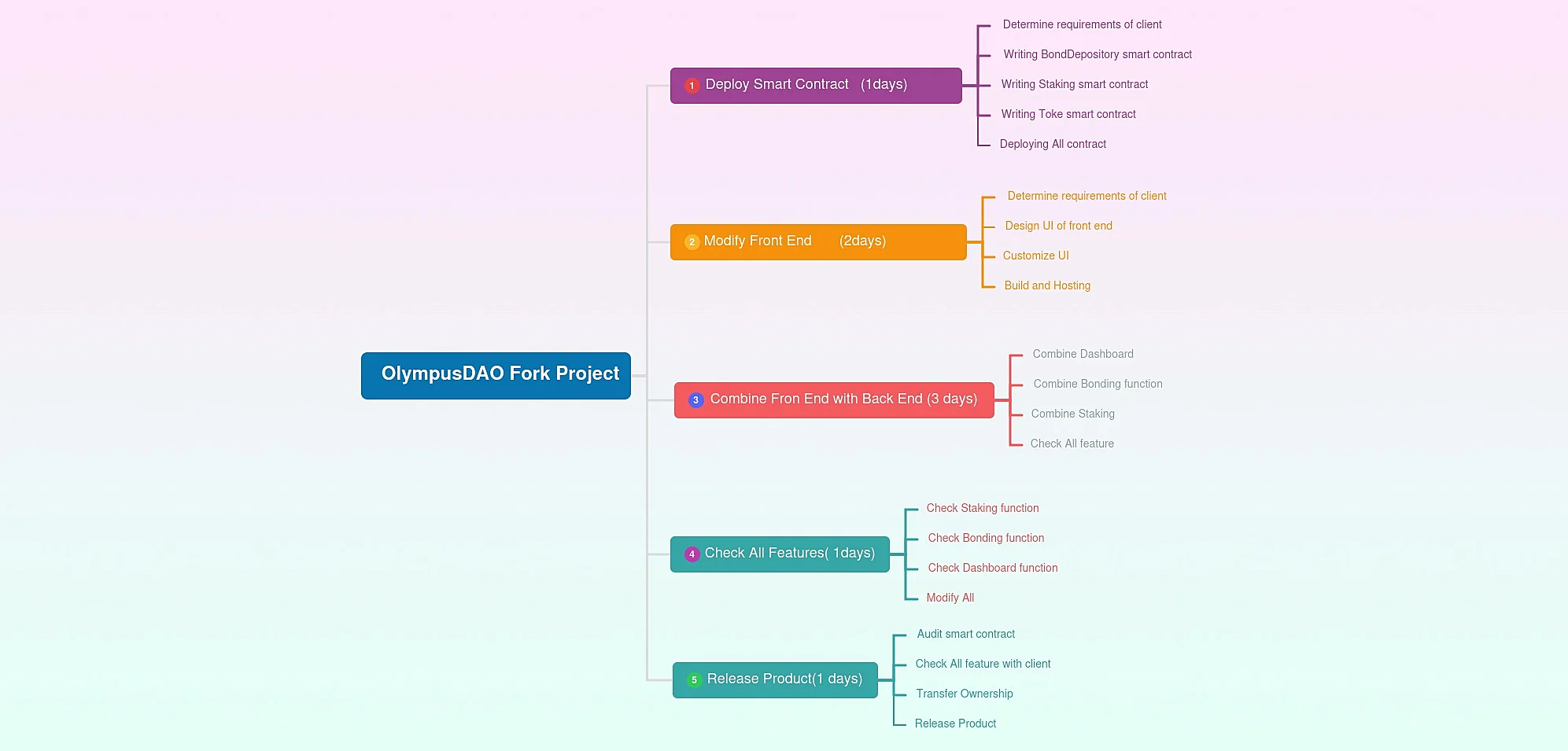
- Coin Market Assessment
Coin Market Cap For a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, market capitalization (or market cap) is the total value of all the coins that have been mined. It's calculated by multiplying the number of coins in circulation by the current market price of a single coin.
Max Supply The maximum number of coins coded to exist in the lifetime of the cryptocurrency.
Total Supply The amount of coins that have already been created minus the number of coins that have been burned (removed from circulation)
Fully Diluted Valuation Current Price x Max Supply
APY The annual percentage yield (APY) is the real rate of return earned on an investment, taking into account the effect of compounding interest. Unlike simple interest, compounding interest is calculated periodically and the amount is immediately added to the balance.
TVL Total value locked (TVL), in the context of cryptocurrency, represents the sum of all assets deposited in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols earning rewards, interest, new coins and tokens, fixed income, etc. ... The metric is an important gauge of the overall DeFi market.
- Developing Crypto
Development Factors Aside from technical integrations, security & compliance approaches play a major part in a successful hosted crypto development. Most businesses that want to develop a crypto arm are interested in either A) developing an ICO to raise money for their business project. They generally will require an exchange, wallet, token developed. B) To host an exchange/wallet/token in order to free up fiat based trade costs and controls. or C) For the purposes of Data &/or Asset management.
Hosting Factors awareness of future hosting costs noting that the processing requirement could acculumate. As a ballpark estimate of what is to come regarding hosting costs for a blockchain once the development is live, expect anywhere from $350-$7000 AUD /month on hosting although every project is different, however if that were the case the [1]% transaction fees could (as a ballpark estimate) outshine that cost by 100x. Digital whitepaper & ICO marketing could also be an additional expected ongoing cost to help facilitate that success. Here is one guide regarding blockchain hosting fees https://aws.amazon.com/managed-blockchain/pricing/ethereum/
Global Compliance Look to Oracle.com and legal advice.
Development Pricing Crypto developments costs should not be underestimated and proceed with caution if presented with a lowball price. If you are in the region of $15k AUD and above then you are in the right ball park. Pricing needs to be provided based on the full scope of requirement.
- Digital Currency Investor How To
Note Here is a step by step basic guide to start investing in Crypto. The example given covers enough hurdles, that once complete would give the user enough perspective to then formulate their own basic understanding of how to manage crypto investing in a multi faceted scenario. The information is in no way intended at all to be investment advice and in fact is hereby advice not to invest this way, as the staked coins can, like all coins, sink in value rapidly or disappear in a 'rug pull' with zero way of getting the money back. There can also be significant and highly negative and impactful tax implications especially in regard to staking. Never invest in Crypto without qualified advice. Always ensure the URL you are at is the official URL and you are inputting the appropriate passwords for that site. Keep any passwords and data recorded clearly and safely. You should not give access to anyone else. Apps like Koinly could help you to extract data for taxation purposes but ask your accountant. Do your own research. Your decisions are yours and nobody elses so be wary of influence. Understand the risks of making a transactional error like wrong address or correct address on the wrong network for example, wherein, you will lose your money.
The Pathway To Purchasing a TOKEN
For the purpose of this 'Investor How To' demonstration we are going to use the mock example that someone would want to purchase a token, in this case the token is available via the exchange called 'Trader Joe' and the token is not available on the largest exchange (Binance) so the ensuing work around is required and they want to stake and wrap the token. The example is intended to be an extensive process for making a more complex trade, if the user can navigate a trade like this they will have a much better understanding by then of how to trade for basically any scenario they choose.
1) Binance
The only reason Binance is referenced is because it is the most popular exchange for general trading, it's thorough, has respectable rates and widely adopted by cryptocurrencies and worldwide usership. Do your own research and choose your own core exchange. Start an account in Binance and move some cash (fiat) into the account via the deposit tab, you will get the binance address from there and then go to your banks app to manage the forwarding of Fiat to that (in this case, email) address (follow the instructions provided by binance and your bank). You'll need to become accustomed to self managing your Crypto. This step will be your first challenge. Become a strong problem solver. Use Google when stuck. Always do small test transactions to ensure the trade pathway works the way it should.
2) Standard Coin Trading
via binance > wallet > fiat & spot section
3) Advancing Toward a token trade or a complex trade that's not available in Binance
Binance > Buy AVAX currency (via binance > wallet > fiat & spot section)
4) MetaMask
Open a MetaMask wallet. Add the Avalanche network to the Metamask wallet. Withdraw the AVAX from Binance > metamask wallet.
5) Trader Joe
Connect metamask to Trader Joe. Trader Joe - swap AVAX for Token of choice (keep some AVAX here. Fees are paid with AVAX.)
6) Token
Open token app > connect token wallet > you could then stake the tokens, you could then wrap the tokens but you may need to integrate abracadabra too (Remember you'll need some AVAX spare in Metamask for any transfer fees when staking too.).
NEED HELP WITH A CRYPTO PROJECT?
Sumo Media have experience with complex cryptocurrency developments and a trusted & committed team. We can help with a clear outlook, knowledgable advice, well considered & experienced approach, respectable timeline estimations, professionally managed and we reliably deliver project outcomes within the agreed specification. Please request if interested in a list of our previous crypto projects.
